Use of urinary hippuric acid and o-/p-/m-methyl hippuric acid to evaluate surgical smoke exposure in operating room healthcare personnel
圖文摘要說明
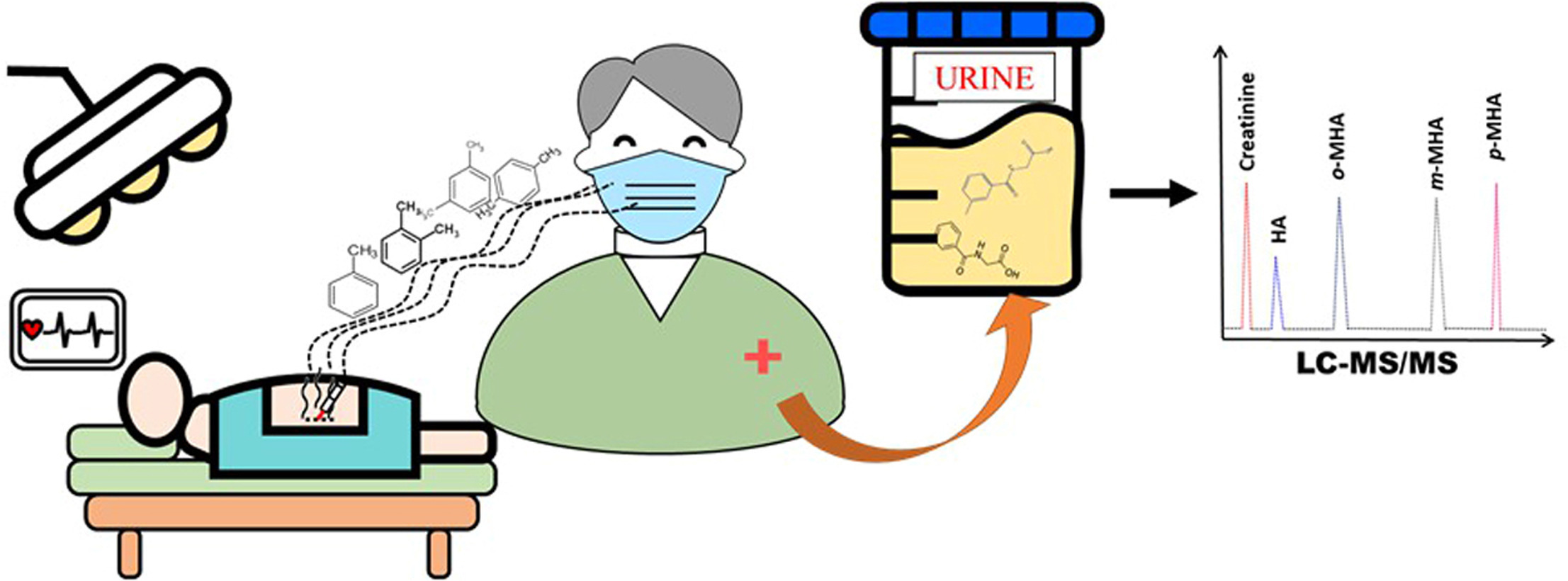
這張示意圖描繪了一項旨在評估手術室醫護人員因暴露於「手術煙霧」(surgical smoke)所產生健康風險的研究。由於手術煙霧中常含有甲苯(Toluene)與二甲苯(Xylene),它們在人體內會分別代謝為馬尿酸(HA)與甲基馬尿酸(MHA),因此可藉由檢測尿液中這兩種代謝物來評估暴露程度。研究流程如圖所示:研究人員收集了160位手術室工作者(包含行政人員、手術護理師、麻醉護理師與外科醫師)的尿液樣本,並利用液相層析串聯質譜儀(LC-MS/MS)技術進行同步定量分析。研究結果顯示,尿液中馬尿酸(HA)濃度最高者竟是行政人員,顯著高於外科醫師;而在甲基馬尿酸(MHA)濃度方面,則是手術護理師顯著高於其他組別。此外,研究也發現醫護人員的職別、性別與年齡皆與尿中代謝物的濃度變化有關,這項發現綜合提醒了所有手術室工作者,皆應警覺並重視手術煙霧的潛在暴露風險。
Abstract
Toluene and xylene are common components of surgical smoke, whereas hippuric acid (HA) and methylhippuric acid (MHA) are the products of toluene and xylene metabolism in humans, respectively. HA and MHA can be used as indicators to evaluate the exposure hazards of toluene and xylene. In this study, we used liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) to simultaneously analyze the HA, o-/m-/p-MHA, and creatinine contents in the urine of healthcare personnel. Concentrations of HA and o-/m-/p-MHAs were normalized to those of creatinine and used to analyze urine samples of 160 operating room (OR) healthcare personnel, including administrative staff, surgical nurses, nurse anesthetists, and surgeons. The results showed that the five analytes could be accurately separated and exhibited good linearity ($r > 0.9992$). The rate of recovery was between 86% and 106%, and the relative standard deviation was less than 5%. Urine from administrative staff presented the highest median concentration of hippuric acid (0.25 g/g creatinine); this was significantly higher than that found in the urine of surgeons (0.15 g/g). The concentrations of urinary o-/m-/p-MHAs in surgical nurses were higher than those in administrative staff, nurse anesthetists, and surgeons. Furthermore, the type, sex, and age of healthcare personnel were associated with changes in urine HA and o-/m-/p-MHA concentrations. Healthcare personnel should be aware of the risk of exposure to surgical smoke.
Keywords: Surgical smoke; Toluene; Xylene; Hippuric acid; Methylhippuric acid; LC-MS/MS

