Target and non-target analysis with molecular network strategies for identifying potential index compounds from Momordica charantia L. for alleviating non-alcoholic fatty liver
圖文摘要說明
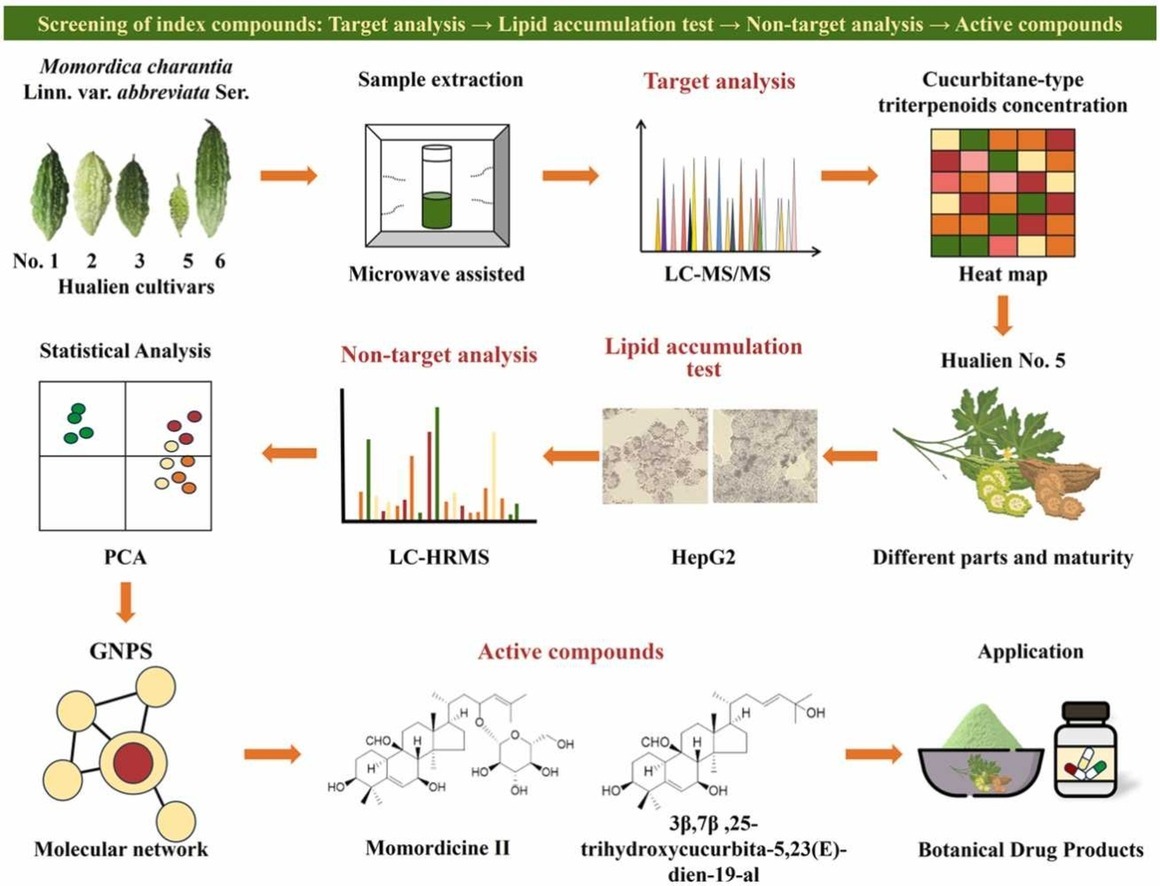
圖片流程圖展示苦瓜(Momordica charantia Linn.)中葫蘆烷型三萜類化合物的篩選與活性研究。透過微波輔助萃取,利用 UPLC-MS/MS 進行目標分析,LC-HRMS 結合 GNPS 進行非目標分析。結果顯示花蓮 5 號苦瓜的葫蘆烷型三萜類含量最高,且不同部位和成熟度的花蓮 5 號苦瓜(除未成熟全果外)均能顯著抑制油酸誘導的肝細胞脂質累積。藤蔓的活性最強,透過非目標分析鑑定出 3β,7β,25-三羥基葫蘆-5,23(E)-二烯-19-醛和苦瓜素 II 為改善非酒精性脂肪肝的活性成分,可應用於植物藥產品開發。
Abstract
The cucurbitane-type triterpenoids of Momordica charantia Linn. have blood lipid lowering effect and thereby improving non-alcoholic fatty liver. In this study, microwave-assisted extraction efficiently obtained these compounds which were further confirmed by the use of UPLC-MS/MS for target analysis and LC-HRMS for non-target analysis, combining GNPS techniques. The results indicated that the content of cucurbitane-type triterpenoids in bitter melon Hualien No. 5 was the highest among the others. Except for the immature whole fruit, the other plant parts such as fruits, seeds, vines and the whole plant of Hualien No. 5 with different maturity levels of immature, mature and overripe can significantly inhibit lipid accumulation in hepatocytes induced by oleic acid. The vines were proven as the most significant among the others where the active components for improving non-alcoholic fatty liver were rapidly screened and identified as 3$\beta$,7$\beta$,25-trihydroxycucurbita-5,23 (E)-dien-19-al and Momordicine II through non-target analysis, multivariate analysis and molecular network.
Keywords:Bitter melon;Non-target analysis;Ultraperformance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS);Liquid chromatography tandem high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS);Global Natural Products Social (GNPS);Non-alcoholic fatty liver

