Effects of Sweet Potato Leaf Extracts and Chlorogenic Acid on Glucose Uptake in C2C12 Cells
圖文摘要說明
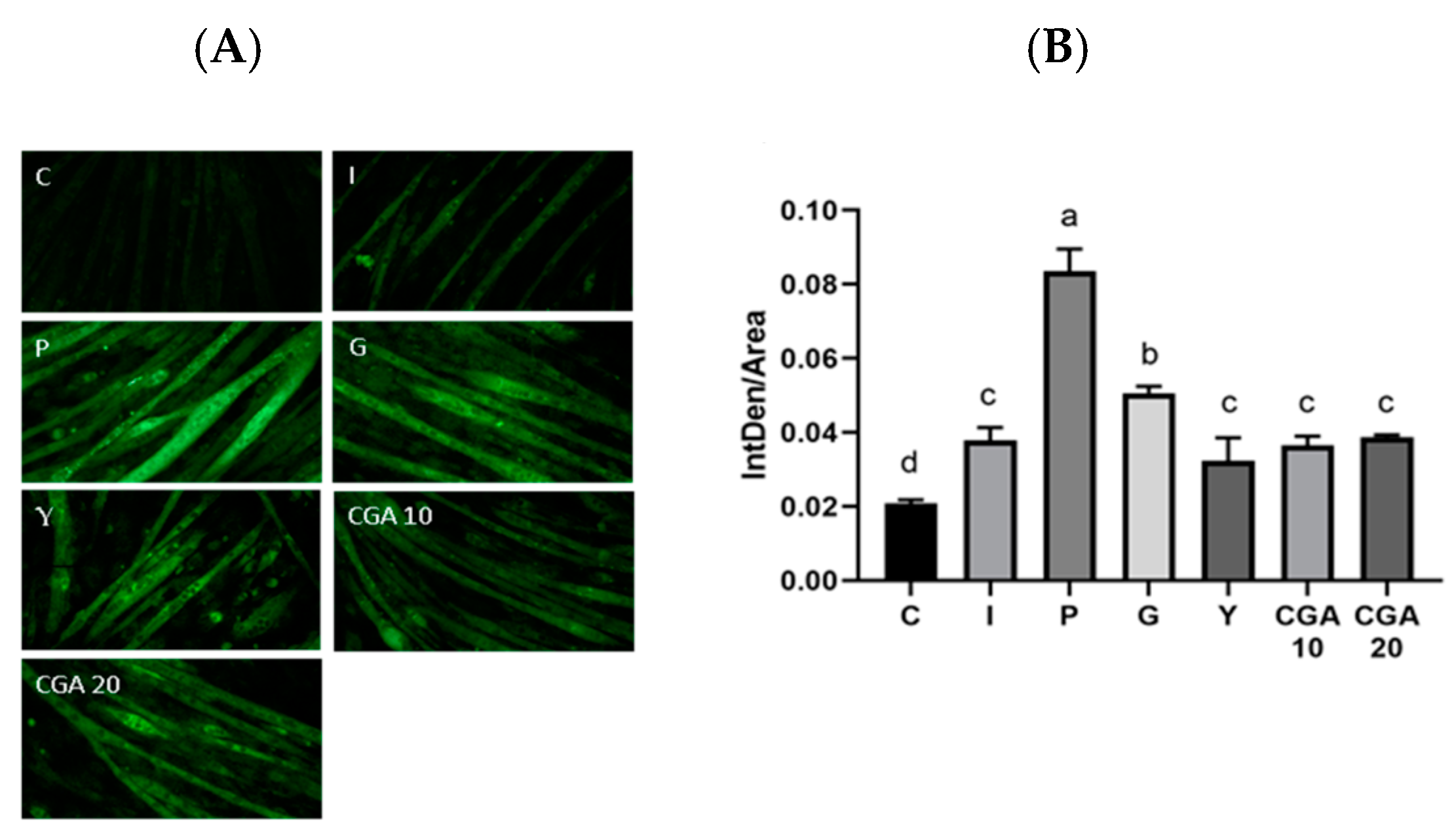
圖片包含 (A) 不同處理組 C2C12 細胞的螢光顯微鏡圖像,顯示葡萄糖類似物 2-NBDG 的攝取情況,以及 (B) 對應的定量分析長條圖,表示每單位面積的螢光強度 (IntDen/Area)。處理組包括對照組 (C)、胰島素組 (I)、紫甘薯葉提取物組 (P)、綠甘薯葉提取物組 (G)、黃甘薯葉提取物組 (Y) 以及不同濃度的綠原酸組 (CGA 10, CGA 20)。長條圖中的不同字母 (a, b, c, d) 表示組間存在顯著差異。摘要指出,紫甘薯葉和綠甘薯葉提取物能有效促進胰島素刺激下的葡萄糖攝取。
Abstract
Edible sweet potato leaf can be exploited in the management and treatment of insulin resistance. This study investigated the effects of three sweet potato leaf extracts (SPLEs) and chlorogenic acid (CGA) on glucose uptake (2-NBDG uptake and GLUT4 abundance) and expression of their related regulatory factors (such as IR, IRS-1, p-Akt1, and p-AMPKα1 abundances) using Western blot analysis in insulin-treated insulin-resistant C2C12 cells. The results show that both purple and green SPLEs improved glucose (2-NBDG) uptake efficacy with insulin treatments, and both SPLEs also increased GLUT4 and IR abundances via activation of p-Akt in the PI3K/Akt pathway, whereas the IR abundance efficacy influence was the same as in the insulin-treated group. The yellow SPLE and CGA have higher protein abundances of IR and IRS-1, while CGA (20 μg/mL) exhibits the highest abundance of p-Akt1 and p-AMPKα1. These results suggest potential benefits of purple and green SPLEs in promoting glucose uptake, possibly through modulation of insulin signaling pathways.
Keywords:sweet potato leaf; insulin resistance; chlorogenic acid; 2-NBDG; GLUT4; PI3K/Akt pathway; type 2 diabetes

