Exploring the unique antioxidative and anti-inflammatory properties of aging black lemon (Citrus limon L. Brum. F.)
圖文摘要說明
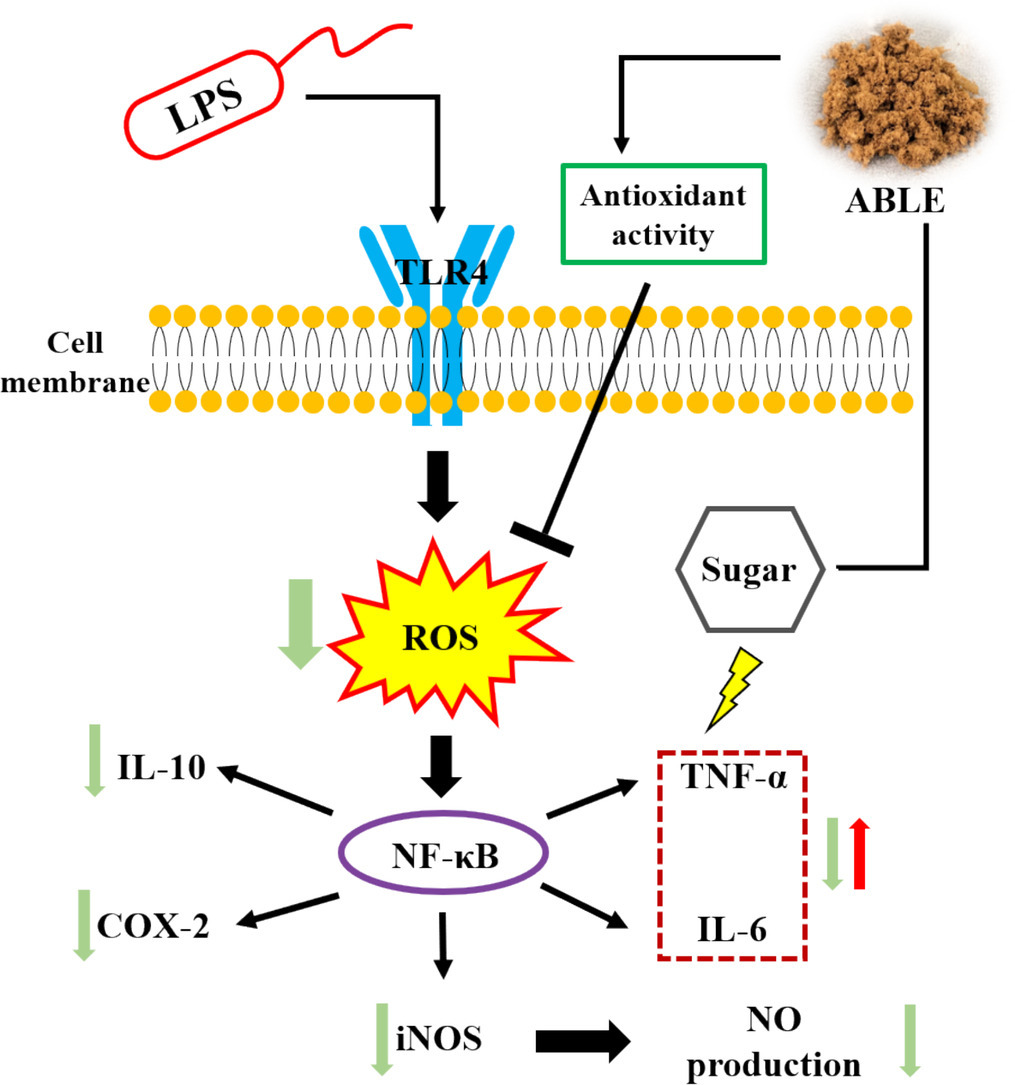
圖中顯示,脂多醣 (LPS) 會激活細胞膜上的 TLR4 受體,進而產生活性氧 (ROS) 和促炎介質,如 TNF-α 和 IL-6。黑檸檬提取物 (ABLE) 具有抗氧化活性,可以抑制 ROS 的產生。此外,ABLE 還可以抑制 NF-κB 的活化,從而減少 iNOS 的表達和 NO 的產生,並降低促炎細胞因子 TNF-α 和 IL-6 的水平。圖中還顯示,ABLE 可以增加抗炎細胞因子 IL-10 的表達。總體而言,此圖說明了黑檸檬提取物通過多種途徑發揮抗炎作用。
Abstract
The aging black lemon is a dried citrus fruit, generally made from lemon, which is lightly thermal processed until it takes on the appearance of blackish-brown leather. This study aimed to determine the phenolic and flavonoid components in aqueous black lemon extract (ABLE). FRAP was used to determine the antioxidant capacity of ABLE. The effects of ABLE on LPS-induced NO production in macrophages (RAW264.7) were investigated by measuring the amount of nitrite released into the culture medium using the Griess reaction. For the anti-inflammatory effects, pro-inflammatory mediators, including iNOS, TNF-α, and NF-κB, were examined by Western blotting. In addition, UPLC/MS/MS data of ABLE presented higher concentrations of gallic acid, protocatechuic acid, vanillic acid, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, luteolin, naringenin, hesperetin, and diosmetin than fresh lemon. Based on the results, we consider ABLE to have outstanding anti-inflammation properties by polyphenols and flavonoids and is a great functional food for inflammation-related diseases.
Keywords:Aging process; Black lemon; UPLC/MS/MS; Anti-inflammatory; Antioxidant

