The Effect of Thermal Processing on the Saponin Profiles of Momordica charantia L.
圖文摘要說明
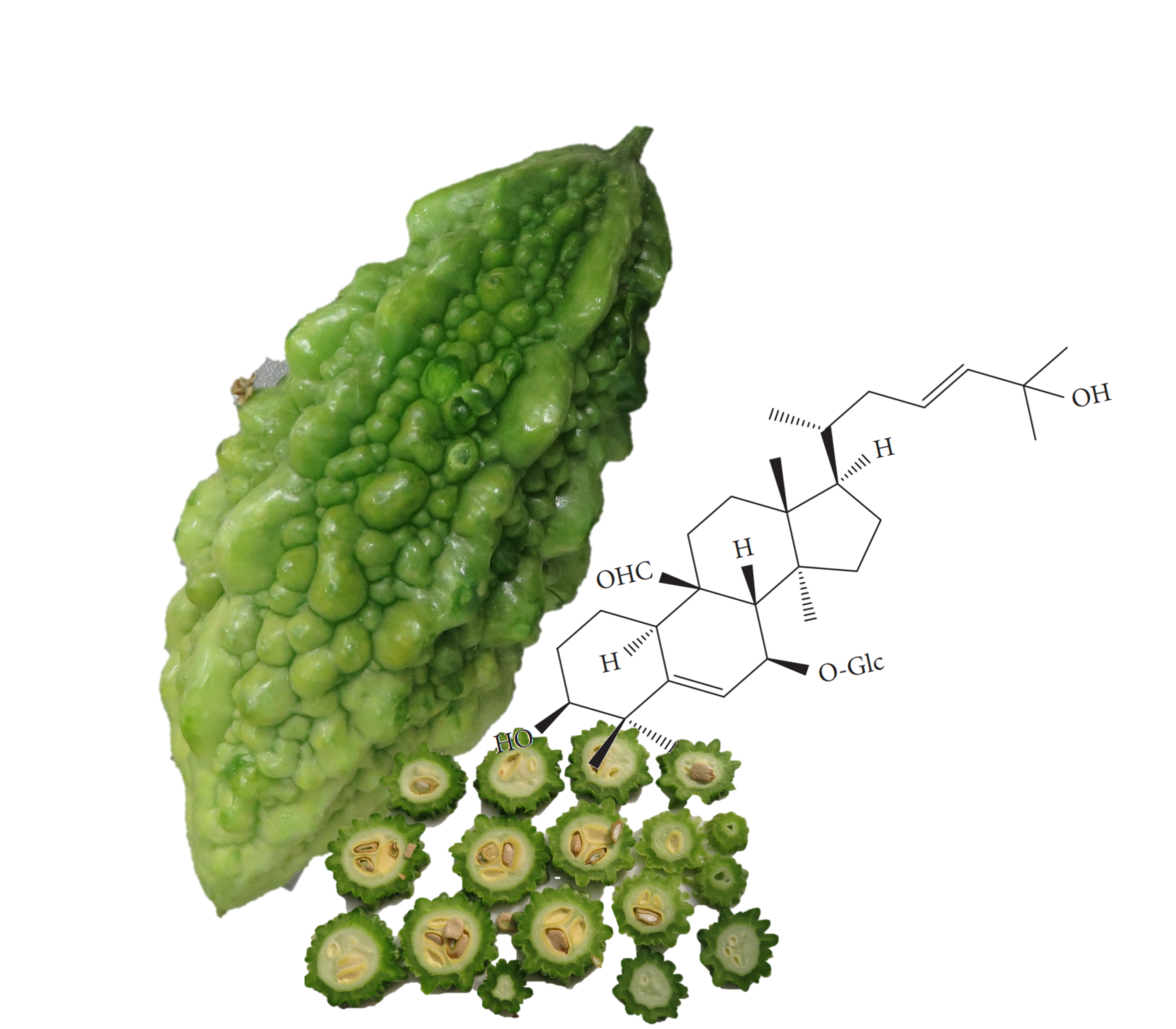
這張圖片呈現了山苦瓜(Momordica charantia L.)的果實及其關鍵的化學成分—皂苷(saponins)。呈現一顆完整的苦瓜,以及數個苦瓜的橫切面切片。在苦瓜的旁邊,繪製了一個皂苷類化合物的化學結構式,皂苷是一類三萜類的糖苷分子,不僅是山苦瓜苦味的來源,也賦予其多種藥理活性。
Abstract
Saponins from Momordica charantia L. are a class of triterpenoid glucoside molecules that contribute to the bitter flavour of the plant and possess pharmacological properties. However, little is known about how the bioactivity and bitter flavour of saponins are affected by thermal processing. We established saponin profiles in bitter gourd extracts using a UPLC-ESI-MS/MS method. Seven saponins including momordicoside F1, momordicoside F2, momordicoside I, momordicoside K, momordicoside L, 3β,7β,25-trihydroxycucurbita-5, 23(E)-dien-19-al, and momordicine I were monitored for the effects of thermal processing on their stabilities. The results showed that both 3β,7β,25-trihydroxycucurbita-5,23(E)-dien-19-al and momordicoside L were extremely sensitive to heat treatment, particularly when they were heated at 100°C for more than 10 mins and under 121°C for 20 mins. Other saponins were reduced significantly by autoclaving, but they remained unchanged at lower temperatures. In conclusion, specific bitter gourd saponins are affected by thermal treatment, which may modify the bioactive components or bitter flavour of the bitter gourd extracts.
Keywords:Saponins; Momordica charantia L.; UPLC-ESI-MS/MS; Thermal processing

