Analysis of Chlorogenic Acid in Sweet Potato Leaf Extracts
圖文摘要說明
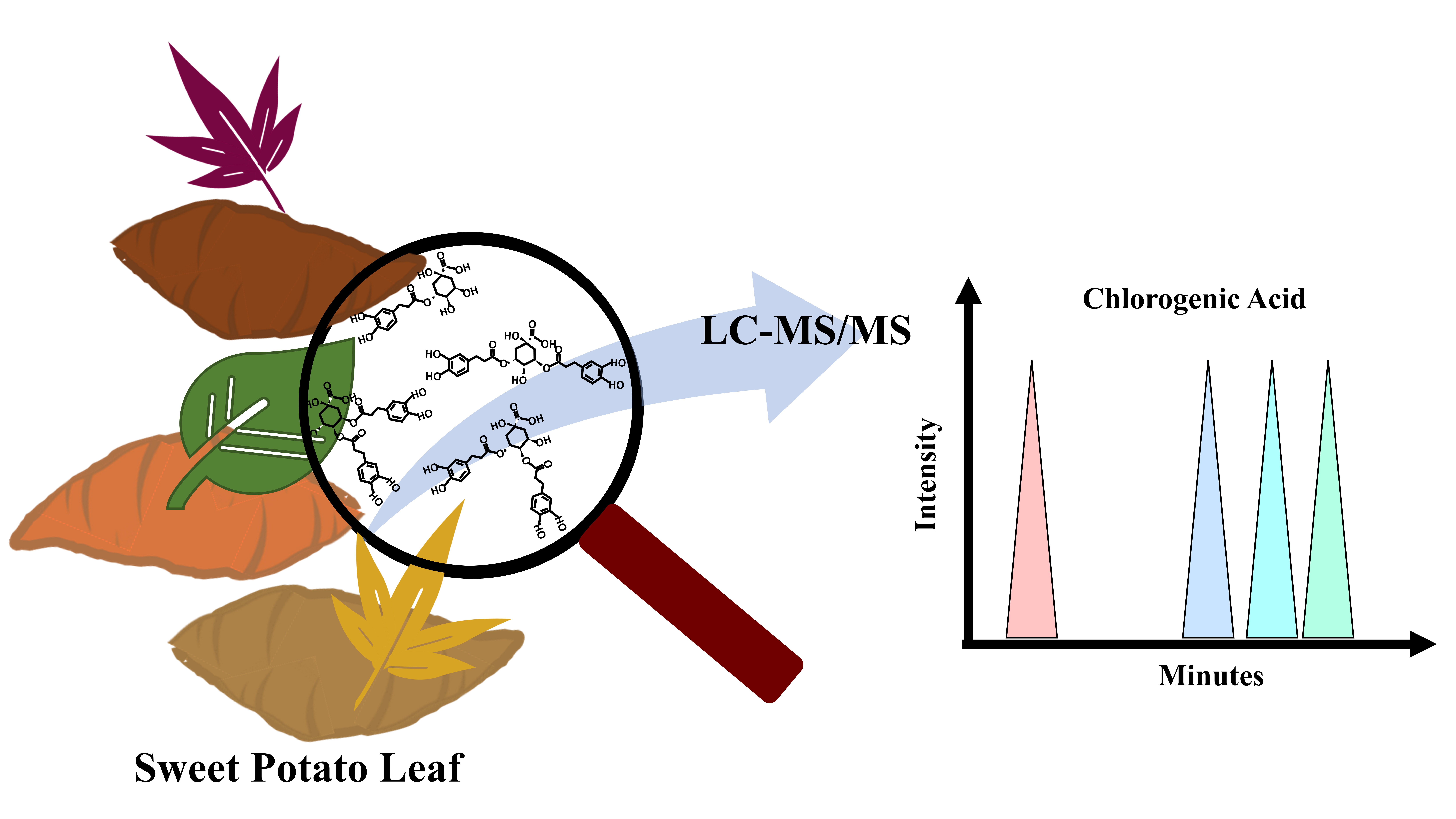
這張圖片展示了利用液相色譜串聯質譜 (LC-MS/MS) 分析不同品種甘薯葉中綠原酸 (Chlorogenic Acid, CGA) 活性成分的過程。圖中左側呈現了不同顏色的甘薯葉(紫色、綠色和黃色),並通過放大鏡突顯了其中的綠原酸類化合物的分子結構。箭頭指向 LC-MS/MS 分析,右側的色譜圖示意性地展示了在不同保留時間洗脫出來的綠原酸及其異構體的訊號峰強度。這項研究旨在鑑定和比較不同甘薯品種葉片中綠原酸類化合物的組成和含量差異。
Abstract
Sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.) is one of the most important food crops worldwide, with leaves of different varieties showing purple, green and yellow, and these leaves provide a dietary source of nutrients and various bioactive compounds. The objective of this study was to identify the active constituents of chlorogenic acids (CGAs) in different methanolic extract of leaves of three varieties of sweet potato (purple CYY 98-59, green Taoyuan 2, and yellow CN 1927-16) using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Genotype-specific metabolite variations were observed; CGAs and three isomeric peaks were detected in sweet potato leaf extracts (SPLEs). Among them, the yellow SPLE contained the highest contents of 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (3,5-di-CQA) and 3,4-dicaffeoylquinic acid (3,4-di-CQA), followed by the green SPLE, whereas the purple SPLE retained lower 3,5-di-CQA content compared to yellow and green SPLEs. All three SPLEs contained lower 4,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid (4,5-di-CQA) and CGA contents compared to 3,5-di-CQA and 3,4-di-CQA, although CGA constituents were not significantly different in genotypes, whereas purple SPLE contained higher 4,5-di-CQA content compared to yellow and green SPLEs. This study indicates that SPLs marketed in Taiwan vary widely in their biological potentials and may impart different health benefits to consumers.
Keywords:sweet potato leaf; chlorogenic acids; liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry

