Quantification of Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis-Related Organic Acids in Human Urine Using LC-MS/MS
圖文摘要說明
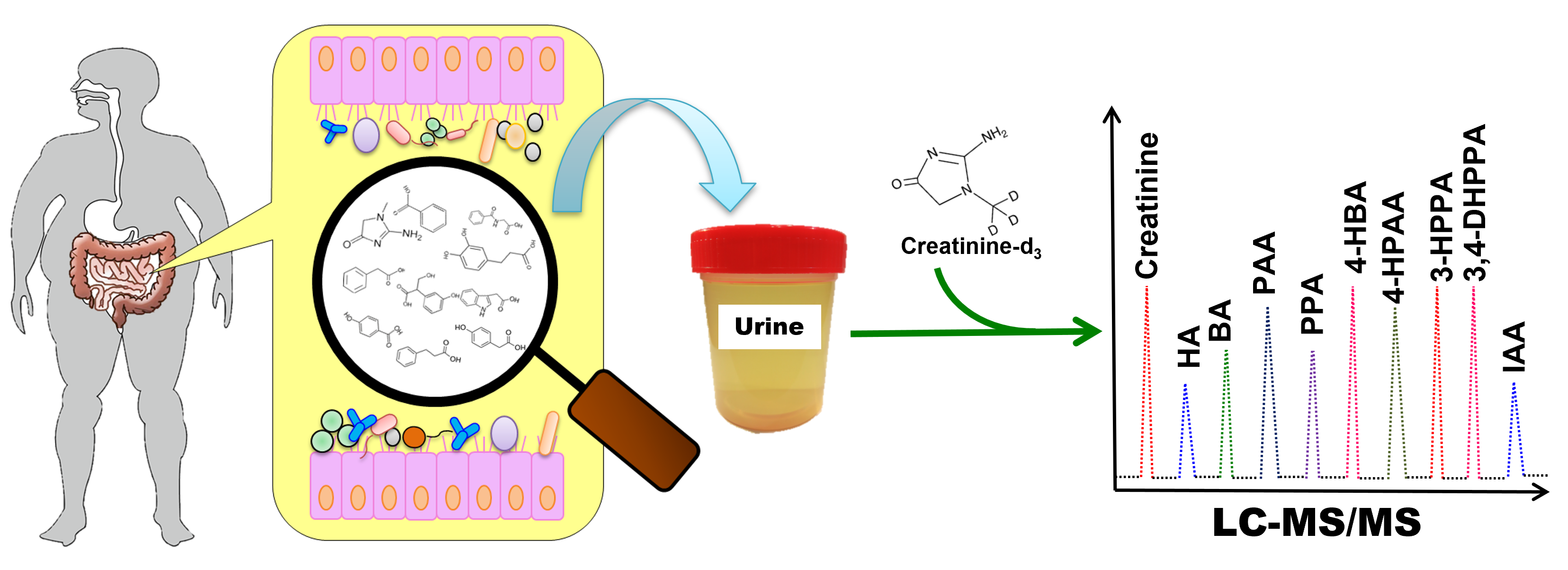
這張圖片展示了透過尿液分析腸道代謝物的流程:人體腸道產生的代謝物經尿液排出,收集尿液樣本並加入內標物(如Creatinine-d3)後,利用液相層析串聯質譜儀(LC-MS/MS)進行分析,以鑑定和量化尿液中如Creatinine(肌酸酐)、HA(馬尿酸)、BA(苯甲酸)、PAA(苯乙酸)、PPA(苯丙酸)、4-HBA(4-羥基苯甲酸)、4-HPAA(4-羥基苯乙酸)、3-HPPA(3-羥基苯丙酸)、3,4-DHPPA(3,4-二羥基苯丙酸)、IAA(吲哚乙酸)等特定腸道代謝物。
Abstract
Urine organic acid contains water-soluble metabolites and/or metabolites—derived from sugars, amino acids, lipids, vitamins, and drugs—which can reveal a human’s physiological condition. These urine organic acids—hippuric acid, benzoic acid, phenylacetic acid, phenylpropionic acid, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 4-hydroxyphenyl acetic acid, 3-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid, 3,4-dihydroxyphenyl propionic acid, and 3-indoleacetic acid—were the eligible candidates for the dysbiosis of gut microbiota. The aim of this proposal was to develop and to validate a liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) bioanalysis method for the nine organic acids in human urine. Stable-labeled isotope standard (creatinine-d3) and acetonitrile were added to the urine sample. The supernatant was diluted with deionized water and injected into LC-MS/MS. This method was validated with high selectivity for the urine sample, a low limit of quantification (10–40 ng/mL), good linearity (r > 0.995), high accuracy (85.8–109.7%), and high precision (1.4–13.3%). This method simultaneously analyzed creatinine in urine, which calibrates metabolic rate between different individuals. Validation has been completed for this method; as such, it could possibly be applied to the study of gut microbiota clinically.
Keywords:gut microbiota; LC-MS/MS; organic acid; human urine

