The Demethoxy Derivatives of Curcumin Exhibit Greater Differentiation Suppression in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes Than Curcumin: A Mechanistic Study of Adipogenesis and Molecular Docking
圖文摘要說明
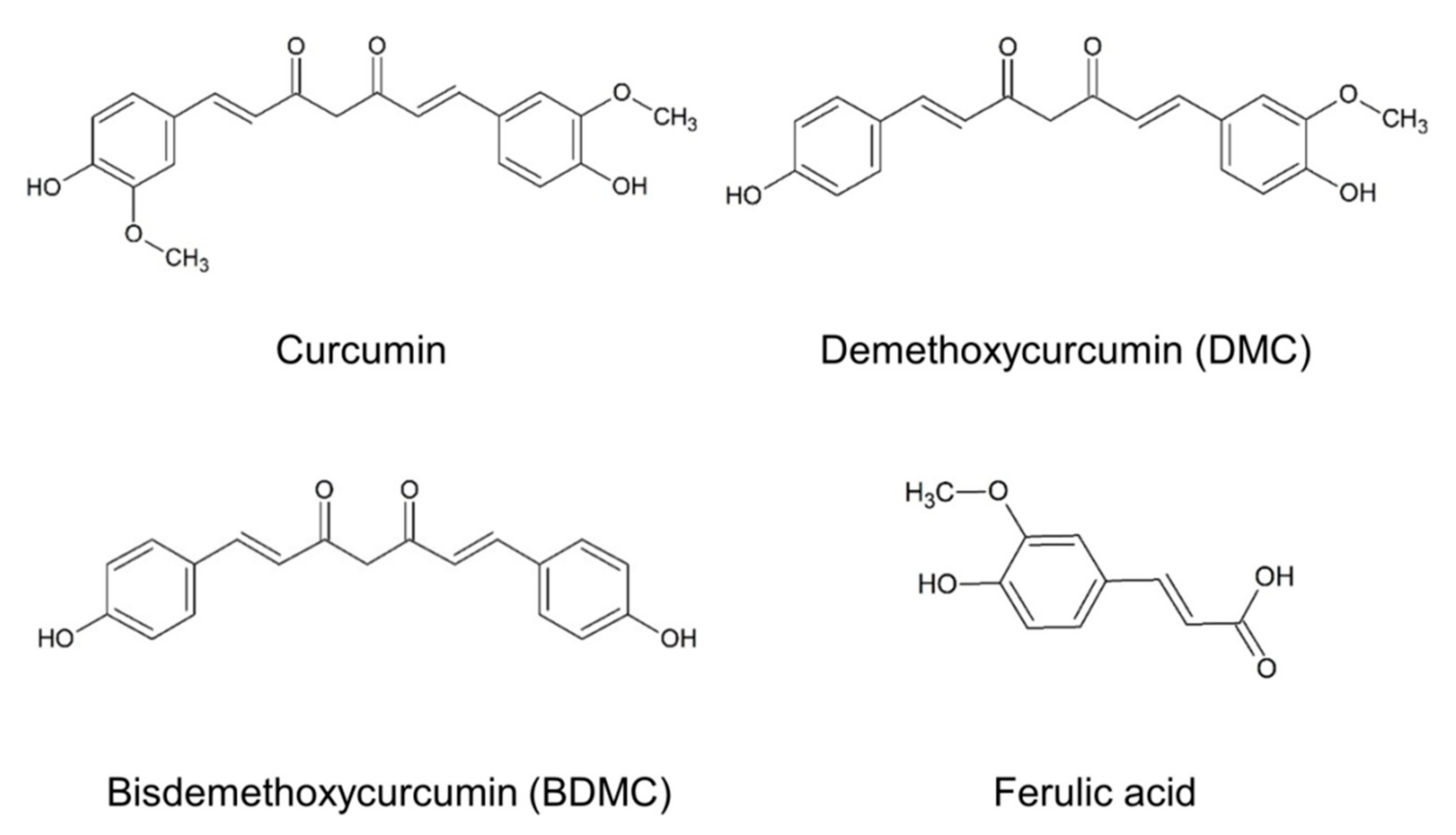
這張圖顯示了本研究中探討的三種主要薑黃素類化合物的化學結構:薑黃素 (Curcumin)、去甲氧基薑黃素 (DMC) 和雙去甲氧基薑黃素 (BDMC),以及相關的阿魏酸 (Ferulic acid),其主要差異在於苯環上甲氧基(-OCH₃)的數量。研究比較了這三種薑黃素在抑制脂肪細胞生成方面的活性,發現 BDMC 的效果最為顯著。
Abstract
Curcumin is a known anti-adipogenic agent for alleviating obesity and related disorders. Comprehensive comparisons of the anti-adipogenic activity of curcumin with other curcuminoids is minimal. This study compared adipogenesis inhibition with curcumin, demethoxycurcumin (DMC), and bisdemethoxycurcumin (BDMC), and their underlying mechanisms. We differentiated 3T3-L1 cells in the presence of curcuminoids, to determine lipid accumulation and triglyceride (TG) production. The expression of adipogenic transcription factors and lipogenic proteins was analyzed by Western blot. A significant reduction in Oil red O (ORO) staining was observed in the cells treated with curcuminoids at 20 μM. Inhibition was increased in the order of curcumin < DMC < BDMC. A similar trend was observed in the detection of intracellular TG. Curcuminoids suppressed differentiation by downregulating the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α (C/EBPα), leading to the downregulation of the lipogenic enzymes acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) and fatty acid synthase (FAS). AMP-activated protein kinase α (AMPKα) phosphorylation was also activated by BDMC. Curcuminoids reduced the release of proinflammatory cytokines and leptin in 3T3-L1 cells in a dose-dependent manner, with BDMC showing the greatest potency. BDMC at 20 μM significantly decreased leptin by 72% compared with differentiated controls. Molecular docking computation indicated that curcuminoids, despite having structural similarity, had different interaction positions to PPARγ, C/EBPα, and ACC. The docking profiles suggested a possible interaction of curcuminoids with C/EBPα and ACC, to directly inhibit their expression.
Keywords:adipocyte; anti-adipogenesis; bisdemethoxycurcumin; curcuminoid; demethoxycurcumin; transcription factor.

