Targeting NF-κB in diabetic nephropathy: exploring the therapeutic potential of phytoconstituents
圖文摘要說明
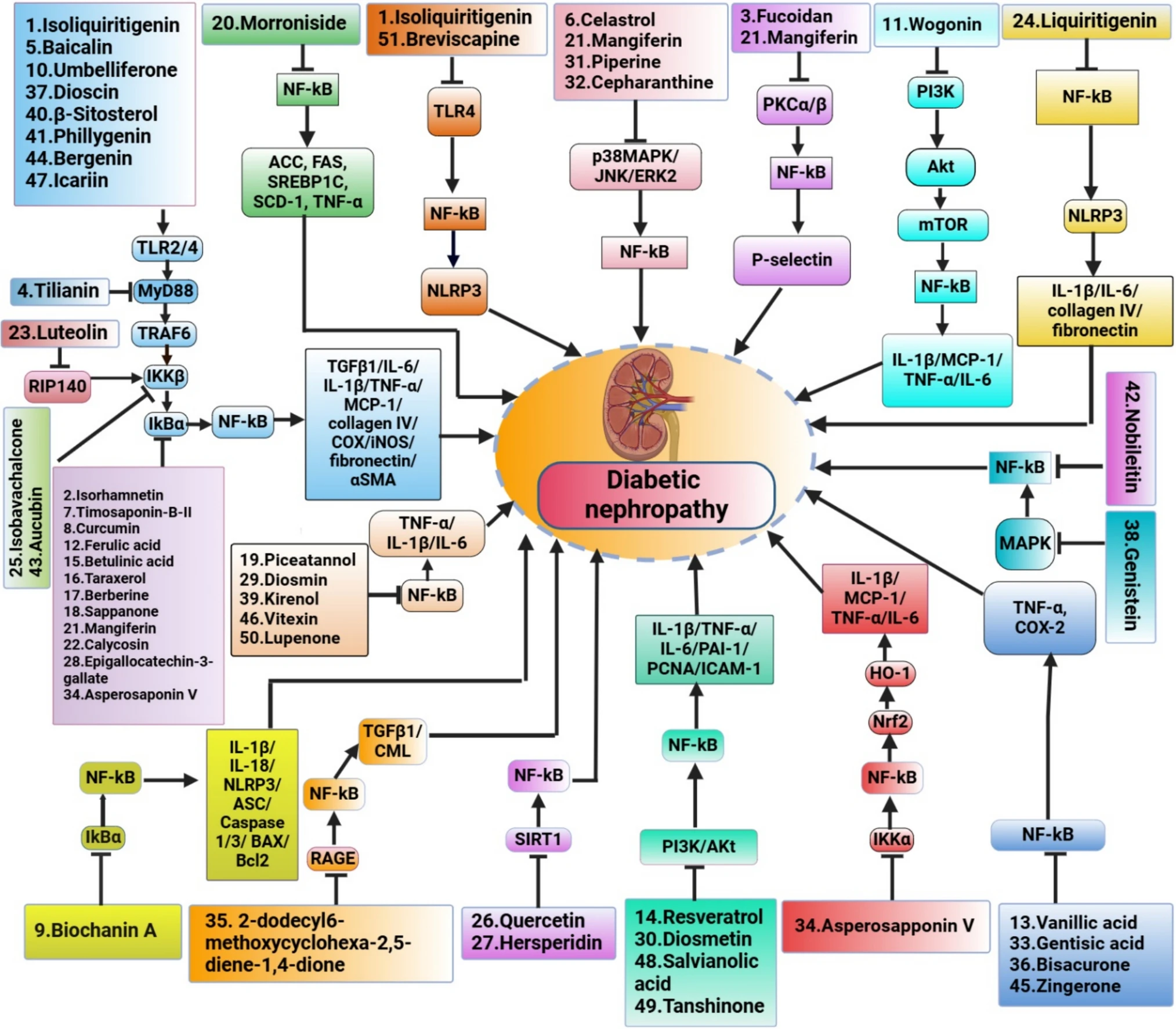
這張精細的圖表全面闡述了多種天然化合物如何透過複雜的分子網絡,對糖尿病腎病變(Diabetic Nephropathy, DN)的病程產生多重調控作用。圖的核心描繪了受損的腎臟器官,並以箭頭指示了多種化合物的介入點及其作用機制。圖中列舉了Isoliquiritigenin、Morroniside、Tilianin、Luteolin、Isoavachalcone、Biochanin A等多種具潛在療效的化合物。這些化合物並非單一靶點作用,而是能影響NF-κB、TLR4、MyD88、TRAF6、RIP140、IKKβ等多條關鍵細胞信號通路。這些通路在糖尿病腎病的炎症、細胞凋亡、氧化應激及纖維化等核心病理過程中扮演關鍵角色。具體而言,圖中展示了這些化合物如何調控TGFβ1、IL-6、TNF-α、MCP-1、COX、iNOS、纖連蛋白和αSMA等致病因子和蛋白質的表達,這些分子是腎臟損傷和纖維化的主要驅動因素。此外,Resveratrol和Asperosaponin V等抗氧化、抗炎化合物,可能透過活化SIRT1、PI3K/Akt或Nrf2/HO-1通路,減輕氧化應激和炎症反應。另一些化合物則可能抑制RAGE通路,減少晚期糖基化終產物(AGEs)對腎臟的損傷。總之,這張圖提供了全面視角,闡明不同天然產物如何透過調節炎症、抑制纖維化、減輕氧化應激及影響細胞存活等機制,干預糖尿病腎病變的發展,為新藥開發提供了重要指引。
Abstract
The growing epidemic of diabetes mellitus and its associated complications presents a major global health challenge. Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is a critical microvascular complication of diabetes, accounts for approximately one-third of all related cases worldwide and frequently progresses to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and premature mortality. Extensive experimental evidence underscores the pivotal role of chronic inflammation driven by the activation of the nuclear transcription factor NF-κB in the pathogenesis of DN. Triggered by various factors including hyperglycemia, NF-κB activation leads to the expression of numerous pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines and cell adhesion molecules, resulting in the pathological hallmarks of DN: podocyte injury, excessive extracellular matrix accumulation, glomerulosclerosis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, renal tubular atrophy and increased proteinuria. Consequently, NF-κB emerges as a promising therapeutic target for DN. Naturally occurring phytoconstituents, as inhibitors of the NF-κB pathway and are gaining significant attention due to their lower toxicity, enhanced safety, greater efficacy and cost-effectiveness. This review summarizes the role of NF-κB in the pathophysiology of DN and examines recent research on medicinal plants and phytoconstituents that target the NF-κB signaling pathway in both in vitro and in vivo and in silico models. Furthermore, we elucidate their mechanisms of action and evaluate their potential as effective therapeutic agents for mitigating DN-related inflammation and complications. This provides a theoretical framework for the development of novel anti-nephropathic drugs that may overcome the limitations of current medications.
Keywords:NF-κB, Diabetic nephropathy, Cytokines, Phytochemicals, Infammation

