The Functional Ability of Stingless Bees (Lepidotrigona) Propolis on Inflammation-Related Disorders
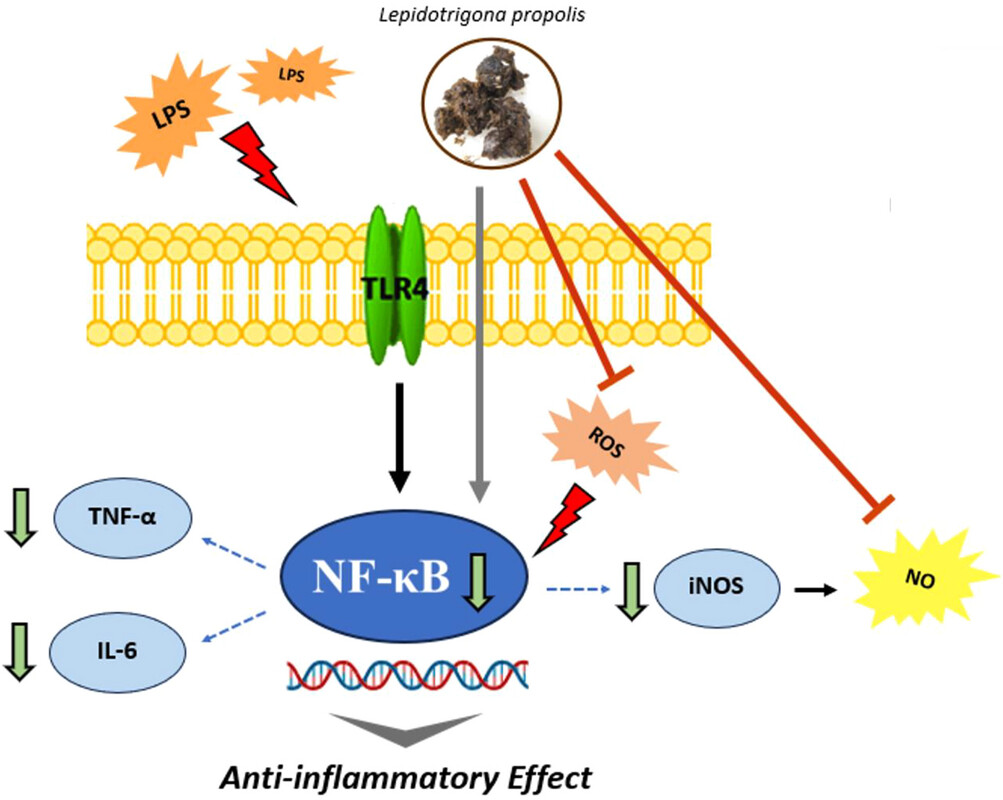
圖文摘要說明
這張圖表是一個作用機制的示意圖,展示了台灣無刺蜂蜂膠(Lepidotrigona propolis)如何透過多個途徑發揮其抗發炎功效:
- LPS 誘導發炎通路: 脂多醣(LPS)刺激細胞膜上的 TLR4 受體,激活下游的發炎核心轉錄因子 NF-κB。
- 蜂膠的抑制作用: 台灣無刺蜂蜂膠介入此通路,主要發揮以下作用:
- 抑制 NF-κB 活化(核心抑制): 蜂膠能直接或間接(圖中灰色箭頭所示)下調 NF-κB 的活性。
- 減少下游發炎介質: 由於 NF-κB 活性被抑制,其下游的發炎介質(如 TNF-α 和 IL-6)的表達被下調(綠色向下箭頭)。
- 抑制 iNOS/NO 通路: 蜂膠能夠抑制 iNOS(誘導型一氧化氮合酶)的表達,進而顯著減少一氧化氮(NO)的生成。
- 清除 ROS: 蜂膠直接作用於細胞內的活性氧(ROS),抑制其產生或清除其自由基,從而減少氧化壓力。
總結: 台灣無刺蜂蜂膠透過多靶點機制,包括抑制 NF-κB 的活化、減少促炎細胞因子(TNF-α, IL-6)和 NO 的生成,以及清除 ROS,達到其顯著的抗發炎效果。
Abstract
The large majority of the bees in the Apidae family are honey bees and stingless bees. Despite honey bees (Apis mellifera) being widely distributed worldwide, Lepidotrigona sp. is a particular genuine stingless bee that can be found only in the Southeast Asia region and Taiwan. Hence, the objectives of this study were firstly to identify Lepidotrigona propolis as an alternative medicine and investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of on lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced RAW 264.7 macrophage cells by the determination of cell viability, dendritic cell morphology, nitric oxide (NO) production, reactive oxygen species (ROS) detection, and inflammation-related proteins analysis. In this study, the polyphenols and flavones in the propolis have been detected by UPLC-ESI-MS/MS. Compared to the LPS group, this propolis type also showed decreased NO and ROS production and a change in cell morphology. Additionally, Lepidotrigona propolis can downregulate the expression of some inflammation-related proteins, such as iNOS, TNF-α, NF-κB, and IL-6. In summary, our study has unveiled the diverse therapeutic properties of Lepidotrigona propolis, particularly its potent anti-inflammatory effects. This discovery opens up a promising avenue for developing a novel therapeutic alternative for human health, instilling hope for the future of medical science.

