Expression of Oryza sativa OsSte12 transcription factor influencing antioxidant enzymes, sugar-related operons, and sugar metabolism in Escherichia coli
圖文摘要說明
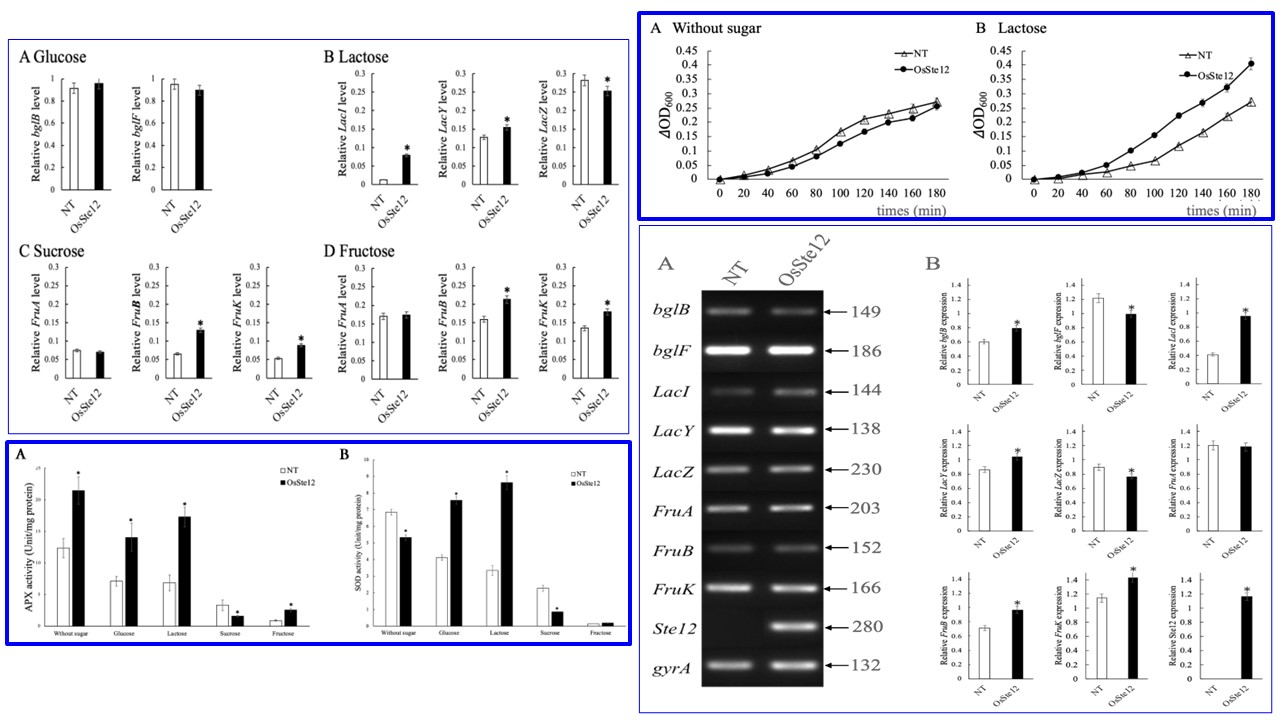
這張圖表綜合分析顯示,水稻基因 OsSte12 的表現能顯著改變微生物宿主的代謝與生理特徵,主要體現在上調乳糖與果糖代謝相關基因的表現,進而促使細菌在乳糖環境下的生長速率大幅提升,同時增強了抗氧化酵素(如 APX 和特定條件下的 SOD)的活性,證明 OsSte12 具有提升宿主碳源利用效率及抗逆境能力的關鍵作用。
Abstract
Ste12 is a C2H2 zinc finger protein transcription factor involved with mating pheromones and regulating protein pathways in microorganisms. Previously, we isolated Ste12 cDNA from rice (Oryza sativa) involved with sugar starvation of α-Amylase in seeds. In this study, we investigated how OsSte12regulated antioxidant enzymes, sugar-related operons, and sugar metabolism by over-expressing OsSte12 in Escherichia coli via transformation. When transformed OsSte12 E. coli was grown in glucose and lactose media, it used these substrates and expressed more activity in ascorbate peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and sucrose synthase compared to a non-transformant (NT) E. coli strain. Moreover, transformants could be grown in lactose for higher ꞵ-galactosidase activity than NTs or in mannitol. In lactose medium, highly-expressed RNA levels of LacI and LacY were found in transformants, while LacZ gene expression in transformants was significantly reduced compared to NTs. In sucrose and fructose media, FruB and FruK transcripts were both significantly higher in transformants than in NTs, whereas FruA transcripts did not show significant differences between transformants and NTs. Compared to NTs, OsSte12transcriptions of all transformants were significantly up-regulated in response to all sugar sources, but transformants were over-expressed more highly when was grown in lactose than in other sugars. Our results are important for elucidating the regulatory mechanisms of sugars and provide new insights into physiological relevance in OsSte12 transformed E. coli.
Keywords: C2H2 zinc fingers; heterologous expressions; lactose; sugar metabolism AcademicPresNotulae Botanicae HortiCluj-NapocaAgrobotanici

