Sources and components of volatile organic compounds in breast surgery operating rooms
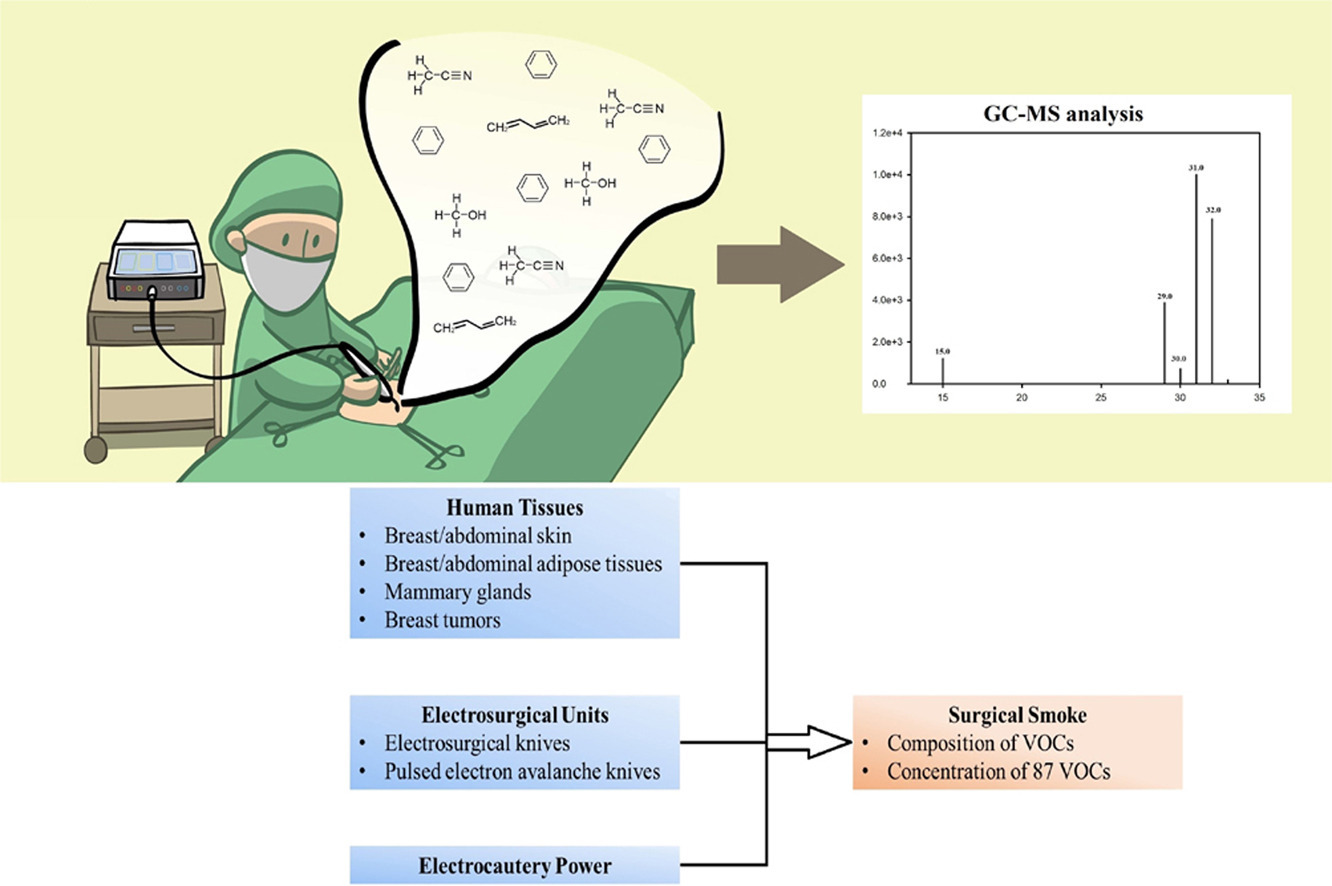
圖文摘要說明
如圖所示,研究人員從23位乳房手術患者中,收集了在處理四種不同人體組織(如乳腺、皮膚等)、使用兩種電燒刀、並在不同電燒功率下所產生的38個手術煙霧樣本,再利用氣相層析質譜儀(GC-MS)對其中的87種VOCs進行定量分析。研究結果發現,使用傳統電燒刀處理「乳腺」組織時所產生的煙霧,其總VOCs濃度(中位數9953.5 ppb)顯著高於其他組織;同時,其中的致癌物如苯(benzene)、1,3-丁二烯(1,3-butadiene)與氯乙烯(vinyl chloride)的含量也最高。此外,所有煙霧樣本中皆檢測到高濃度的甲醇(methanol),且在處理皮膚組織時,若電燒功率高於27.5瓦,VOCs的濃度也會更高。總體而言,此研究證實了手術煙霧中確實含有多種致癌物,且其濃度會因組織類型、手術設備及功率的差異而有顯著變化,突顯了防護手術煙霧的重要性。
Abstract
Objectives
The composition and concentration distribution of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in surgical smoke had seldomly been reported. This study aimed to investigate the profile of VOCs and their concentration in surgical smoke from breast surgery during electrocautery in different tissues, electrosurgical units, and electrocautery powers.
Methods
Thirty-eight surgical smoke samples from 23 patients performed breast surgery were collected using evacuated stainless steel canisters. The concentrations of 87 VOCs in surgical smoke samples were analyzed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The human tissues, electrosurgical units, and electrocautery power were recorded.
Results
The median level of total VOCs concentrations in surgical smoke samples from mammary glands (total VOCs: 9953.5 ppb; benzene: 222.7 ppb; 1,3-butadiene: 856.2 ppb; vinyl chloride: 3.1 ppb) using conventional electrosurgical knives were significantly higher than that from other tissues (total VOCs: 365.7–4266.8 ppb, $P < 0.05$; benzene: 26.4–112 ppb, $P < 0.05$; 1,3-butadiene: 15.6–384 ppb, $P < 0.05$; vinyl chloride: 0.6–1.8 ppb, $P < 0.05$) using different electrosurgical units. A high methanol concentration was found in surgical smoke generated during breast surgery (641.4–4452.5 ppb) using different electrosurgical units. An electrocautery power of $\ge$ 27.5 watts used for skin tissues produced a higher VOCs concentration (2905.8 ppb).
Conclusions
The surgical smoke samples collected from mammary glands using conventional electrosurgical knives had high VOCs concentrations. The carcinogens (including benzene, 1,3-butadiene, and vinyl chloride) and methanol were found in the surgical smoke samples from different electrosurgical units. The type of electrosurgical unit and electrocautery power used affected VOCs concentrations in surgical smoke.
Keywords:Surgical smoke; Breast surgery; Electrosurgical units; Electrocautery power; Volatile organic compounds.

