Modification of polyacrylonitrile-derived carbon nanofibers and bacteriophages on screen-printed electrodes: A portable electrochemical biosensor for rapid detection of Escherichia coli
合作單位:國立臺灣大學
期刊:Bioelectrochemistry
Abstract
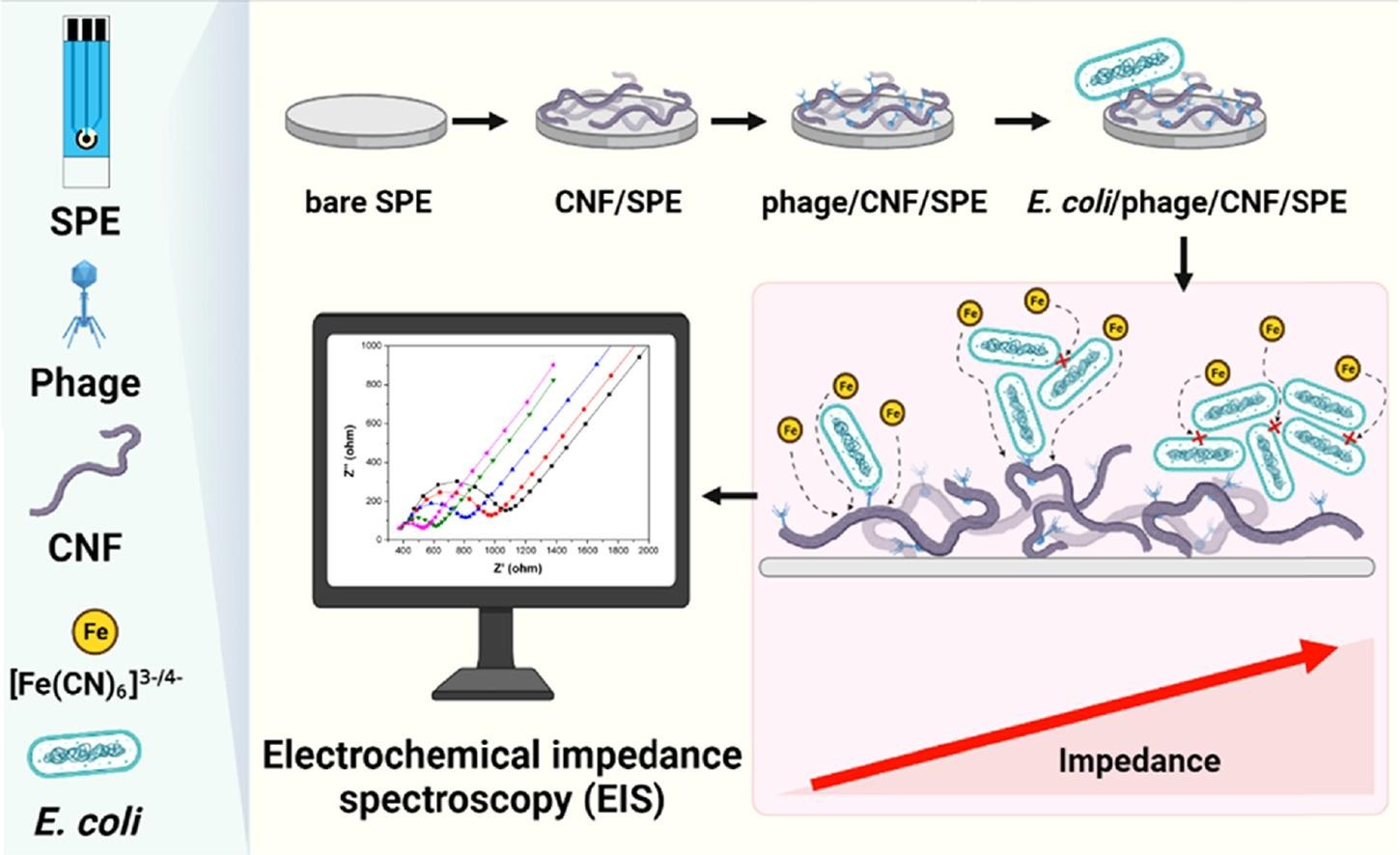
A facile method was developed for fabricating a disposable phage-based electrochemical biosensor for the detection of Escherichia coli. Bare screen-printed electrodes (SPEs) were modified using a two-step drop-casting method, in which polyacrylonitrile-derived electrospun carbon nanofibers (CNFs) were deposited, followed by E. coli bacteriophage immobilization. The deposition of CNFs increased the surface area for bacteriophage immobilization while maintaining a conductive link for ferro/ferricyanide redox transitions. Cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy confirmed that the CNF modification increased the electron-transfer rate, whereas bacteriophages and E. coli blocked electron transfer at the electrode. The biosensor achieved a response within 10 min and a linear response in the E. coli concentration range of 102–106 CFU/mL. A limit of detection (LOD) of 36 CFU/mL in phosphate-buffered saline was achieved, which is the lowest LOD reported thus far for phage-based disposable SPE sensors. The biosensor exhibited recovery rates between 106 % and 119 % for E. coli detection in apple juice. The proposed fabrication method allowed electrodes to be obtained from different production batches with remarkable consistency and reproducibility, and they remained stable at room temperature for one month. Thus, a phage-based disposable SPE that can be used for bacterial detection was developed for the first time.
.

